BASIC DEFINITIONS
LOAD
Any device or circuit that consumes
electric power Or
Any device or apparatus that
draws electric current from supply system is said to impose a load on the
system. The term “LOAD” (in electrical) is used to:
§ To
indicate any device that consumes electrical energy.
§ To indicate power required from given supply
circuit.
§ To indicate the current or power passing
through transmission line.
The load may be resistive,
inductive, capacitive, or some combination of them.
CONNECTED LOAD
It is ‘ the sum of the continuous
ratings of all loads connected to the system or any part thereof.
DEMAND
The demand of an installation of
a system is “the
load that is drawn from the source of supply at the receiving terminals
averaged over a certain period of time”.
e.g., Daily demand, Weekly,
fortnightly, monthly, yearly, etc.
The load may be given in
Ø
Kilowatts (KW)
Ø
Kilovars (KVAr)
Ø
Kilovoltamperes (KVA)
Ø
Kiloamperes (KA)
Ø
Amperes (A)
MAXIMUM DEMAND OR PEAK LOAD
The greatest load drawn during
the specific period of time. For example, the specified demand might be maximum
of all demands such as daily, weekly, monthly, or annual.
Knowledge of maximum demand helps
in determining the installed capacity of a generating stations. The generating
station must be capable of meeting the maximum demand. Hence the cost of plant
and equipment increases with the increase in maximum demand.
DEMAND INTERVAL
It is the period over which the
load is averaged. There are two types of demands:
1. Instantaneous Demand: Demand at any particular time.
2. Sustained Demand: Demand over a certain period of
time.
DEMAND FACTOR (DF)
In
practice consumers do not use all the devices at full load simultaneously. The
maximum demand of each consumer is, therefore, less than his connected load.
The demand factor depends upon the nature of load. Lighting loads have higher
demand factors than power loads. The demand factor is usually less than 1.0
AVERAGE LOAD OR AVERAGE DEMAND
LOAD FACTOR
It is the ratio of the average
load over a given period of time to the maximum demand (peak load) occurring in
that period.
Load factor plays an important
role on the cost of generation per unit (KWh). The higher the load factor, the
lesser will be the cost of generation per unit for the same maximum demand.
DIVERSITY FACTOR
The maximum demands of the
individual consumers of a group are not likely to occur simultaneously. Thus,
there is a diversity in the occurrence of the loads. Due to this diverse nature
of the load, power is never required to supply all connected loads to their
full capacity at the same time.
Diversity factor can be defined
as;
Diversity factor can be defined
for loads, substations, feeders, and generating stations.
The value of diversity factor is
generally greater than 1.0. with a high value representing a good diversity and
1.0 represents a poor diversity.
UTILIZATION FACTOR Fu
It is the ratio of maximum demand
of a system to the rated capacity of the system
The utilization factor can also
be found for a part of the system
PLANT FACTOR OR CAPACITY FACTOR
LOSS
FACTOR
Problem #01
A consumer has the following
connected load:
10 Lamps each of 60 W, 2 Heaters
each of 1000 W, Maximum demand 1500 W. On the average he uses 8 lamps for 5
hours per day. Each heater 3 hours per day. Find: (a) average load. (b) monthly
energy consumption. (c) load factor.
SOLUTION
There
are 4 consumers of diversity having different load requirements at different
timings.
Consumer
#01
Average
load = 1 KW
Maximum
demand = 5 KW at 8 p.m.
Consumer
#02
Maximum
demand = 2 KW at 9 p.m.
Demand
of 1.6 KW at 8 p.m.
Daily
load factor = 0.15
Consumer
#03
Maximum
demand = 2 KW at 12 noon.
load
of 1 KW at 8 p.m.
Average
load of 500 W.
Consumer
#04
Maximum
demand of 10 KW at 5 p.m.
load
of 5 KW at 8 p.m.
Daily
load factor = 0.25.
The
maximum demand of the system occurs at 8 pm. Determine:
1.The diversity factor
2.Average load and load factor of
each consumer
3.Average load and load factor of
the combined load.




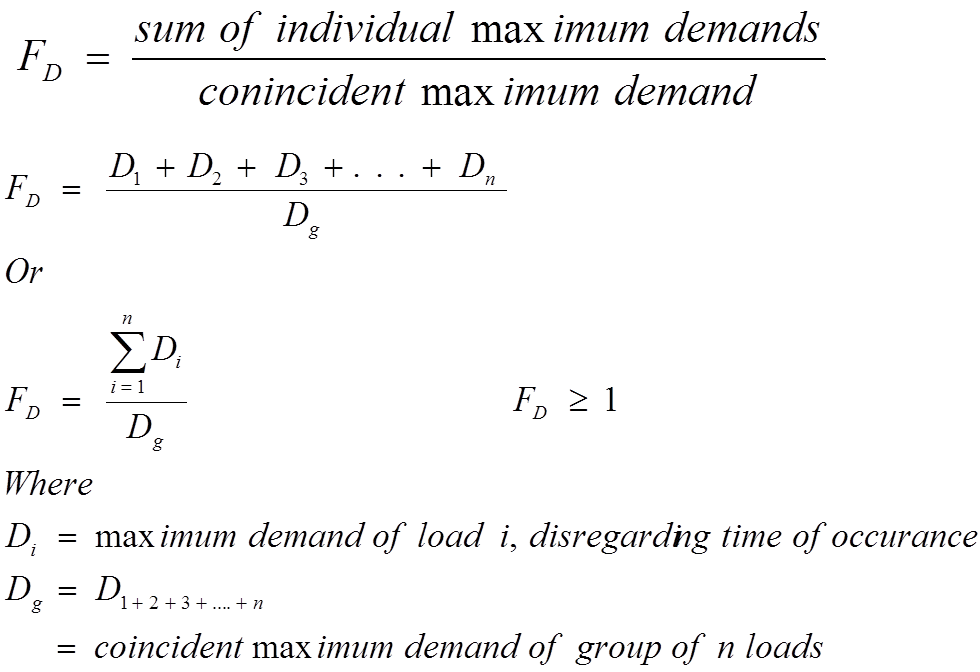




No comments:
Post a Comment